Foundation Drainage in Marysville, OH
Proudly Serving Delaware County & Union County
Foundation drainage can be done many different ways and is important to keep your home and landscape damage free long term. Standing water in the basement not only causes a musty smell while damaging furniture, belongings, floors and walls but can also cause mold. The type of foundation drainage can depend on cost, location of home, and with how much water runoff a home or business will typically get.
Types of Foundation Drainage
French Drain
The French drain is named after its inventor Henry French and is also commonly known as a perimeter drain. A French drain is a perforated sloped drain pipe placed about 8 inches to 2 feet under the foundation covered with gravel or sand to divert water from pooling.

Footing Drainage
A perforated plastic drainage pipe is installed on interior or exterior of the basement / crawlspace walls at floor level. The drainage pipe must have a slope to drain collected water away from structure wrapped with landscape fabric, at least 6 inches of 1/2 inch to 3/4 inch washed gravel covering it and landscape fabric above.
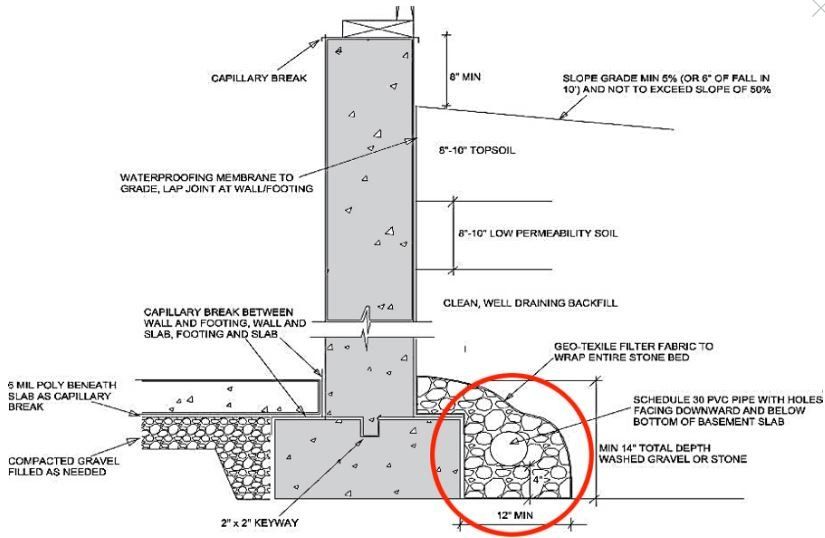
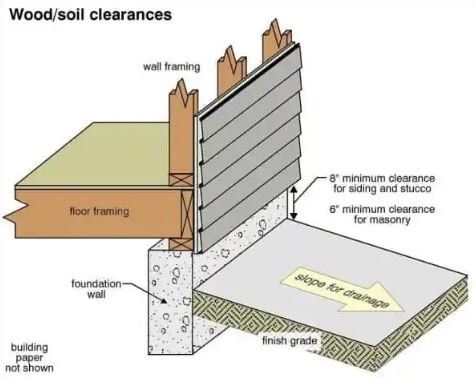
Grading Drainage
Grading Drainage is the easiest system of drainage where gradient is added around the foundation changing the slope around the structure so water will run away from the structure and towards the storm drain. With grading drainage you want 8 inches of minimum clearance for siding and stucco and 6 inches of minimum clearance for masonry.
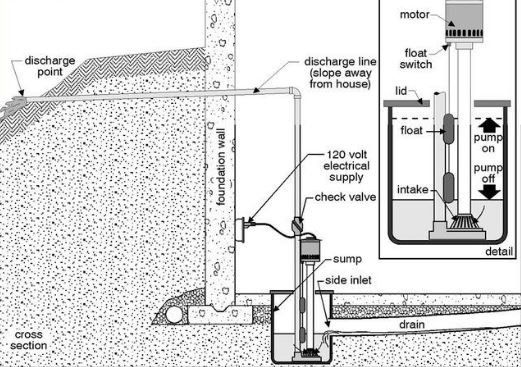
Sum Pit & Pumps
A sump pit is a hole in the basement or crawlspace of a house that collects water that drains in the house or building. The sump pump is electric or battery powered and is triggered when water reaches a certain level moving the water through a perforated pipe near the foundation wall out and away from the house.
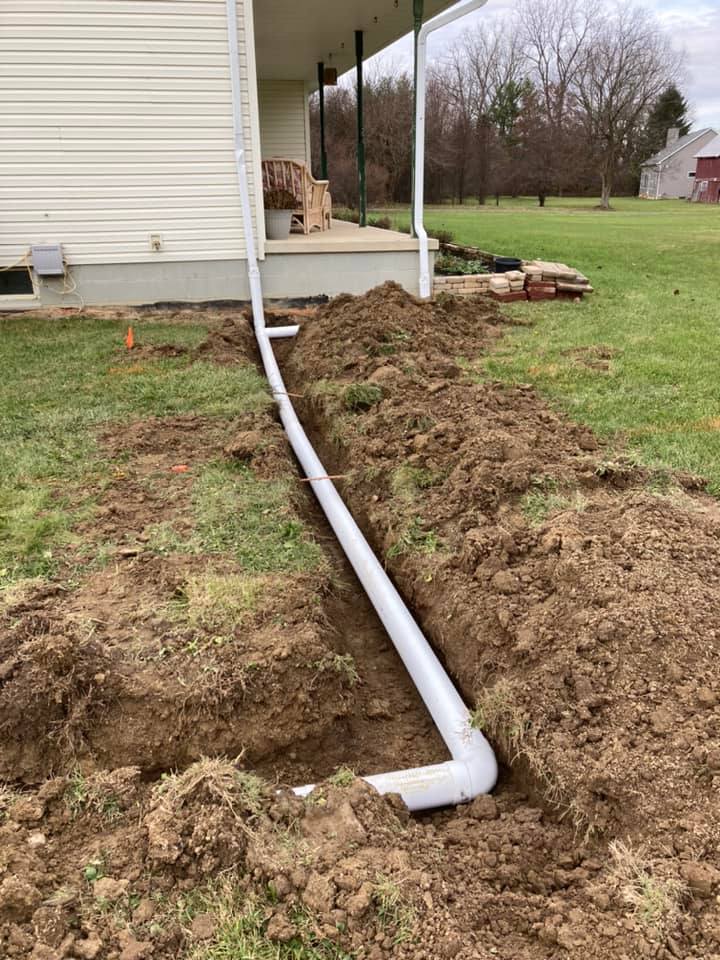
Downspout Drain Lines
Storm water can cause water seepage into crawlspaces and basements if downspout drain lines are not properly installed where necessary. Downspout drain lines are under ground and keep water from pooling on the homes foundation.

How to prevent a wet basement
Improve outside drainage:
- Cleaning gutters to prevent overflow.
- Add downspout extensions to drain water away from foundation.
- Make sure soil around foundation is sloped properly away from house.
Install or replace sump pump:
- A cast-iron sump pump can hold up longer under basement conditions.
- Installing a battery-powered backup pump, in case the power goes out.
Add interior drainage:
- The water is piped to a sump pump that automatically discharges the water outside your house.
Protect against plumbing leaks:
- Replace an old water heater before the interior rusts out and causes a major basement flood.
- Replace rubber washing machine supply hoses if they show signs of cracking.
- Check water supply and drain lines for leaks, and take steps during cold weather to prevent water lines from freezing and bursting.
Install new windows and window well covers:
- Cleaning window wells will prevent them from clogging with leaves and other debris, and can allow water to dry faster.
- Adding a window well cover can prevent water from entering through old leaking windows.
Repair foundation cracks:
Horizontal, vertical, and stair-step cracks in the foundation walls
Check roof for damage:
- Look for worn or missing shingles and other signs of damage that may lead to a roof leak.
MJC Septic Services is a member of the Ohio Onsite Wastewater Association
MJC Septic Services holds an active NPDES Permit. To learn more about NPDES visit the websites below.
Cities We Provide Septic Service To:
- Allen Center, OH
- Arnold, OH
- Ashley, OH
- Berkshire, OH
- Bethlehem, OH
- Big Island, OH
- Broadway, OH
- Byhalia, OH
- Caledonia, OH
- Chuckery, OH
- Claridon, OH
- Delaware, OH
- Essex, OH
- Galena, OH
- Green Camp, OH
- Harlem, OH
- Irwin, OH
- Jerome, OH
- Kibourne, OH
- Kirkpatrick, OH
- La Rue, OH
- Lewis Center, OH
- Magnetic Springs, OH
- Marion, OH
- Martel, OH
- Marysville, OH
- Milford Center, OH
- Morral, OH
- New Bloomington, OH
- New California, OH
- New Dover, OH
- Ostrander, OH
- Peoria, OH
- Pharisburg, OH
- Pottersburg, OH
- Powell, OH
- Prospect, OH
- Radnor, OH
- Raymond, OH
- Richword, OH
- Scioto, OH
- Shawnee Hills, OH
- Unionville Center, OH
- Waldo, OH
- West Jackson, OH
- Woodland,OH
- York Center, OH


